Posts
Corona virus and its updates
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
What is Corona virus? A coronavirus is a kind of common virus that causes an infection in your nose, sinuses , or upper throat. Coronaviruses were first identified in the 1960s, but we don't know where they come from. They get their name from their crown-like shape. Sometimes, but not often, a coronavirus c an infect both animals and humans. Most coronaviruses spread the same way other cold-causing viruses do: through infected people coughing and sneezing , by touching an infected person's hands or face, or by touching things such as doorknobs that infected people have touched. Severe coronavirus outbreaks include: COVID-19: In early 2020, after a December 2019 outbreak in China, the World Health Organization (WHO) identified a new type, 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV), which can be fatal. The organization named the virus severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and named the disease it causes COVID-19. The outbreak qui...
Progeria- A rapid aging
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps

Progeria Introduction Progeria is a rare genetic condition that causes a child's body to age fast. It is an extremely rare autosomal dominant genetic disorder in which symptoms resembling aspects of aging are manifested at a very early age. The word progeria comes from two greek words, Pro & Geras. Pro means before or premature and geras means old age. Also known as Hutchinson- Gilford progeria syndrome (HGPS). It is first described in 1866 by Jonathan Hutchinson. It was also described independently in 1897 by Hastings Gilford that's why later it named as HGPS. Incidence rate Affects in 1 in every 4 million birth worldwide. Facts about progeria The disease can lead to fatal heart complications and heightened risk of stroke. Progeria is incurable but symptoms can be managed. A drug called lonafarnib can extend the average 14 year life expectancy by 1.6 years. Causes HGPS is caused by a mutation in the gene called LMNA (...
Sulfhemoglobinemia- The green blood in body
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps

Sulfhemoglobinemia Introduction It is a rare condition in which there is excess sulfhemoglobin (sulfHb) in the blood. The pigment is a greenish derivative of hemoglobin which cannot be converted back to normal functional hemoglobin. It causes cyanosis even at low blood levels. It occurs when a sulfar atom is incorporated into the Hb molecule. When hydrogen sulfide (H2S) or sulfide ions and ferric ions combine in the blood, the blood is incapable of carrying oxygen . History In 1866, Hoppe- seyler observed the formation of a green product after reaching Hb-O2 with H2S and called this green derivatives sulfhemoglobin (SulfHb). Naturally occuring sulfHb is postulated to be derived from H2S produced by intestinal bacteria, but the mode of formation has not yet been elucidated. Sulf-Hb seldom exceeds 10% of the total Hb present. These sulfheme derivatives exhibit lower affinity towards O2 compared to the native proteins and cannot be reverted to the normal funct...
Presumptive signs of pregnancy
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps

Presumptive signs of pregnancy There are three types of signs to determine the pregnancy. Presumptive Signs Probable Signs Positive Signs Presumptive Signs Usually noted by patients. It is not the proof of pregnancy but the signs to suspect of pregnancy. Also known as early signs of pregnancy. Amenorrhea ( Cessation of menstruation) Earliest clues of pregnancy. No periodic blood after onset of pregnancy. Other causes of amenorrhea are: # Menopause , Stress, Chronic Illness ( TB, endocrine disorders or CNS abnormalities), Anemia, Excessive Exercises 2. Breast Changes Mostly evident on 6-8 weeks of pregnancy Increased size of breast. Vascular engorgement Hyp...
Fetal Circulation | American Heart Association
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
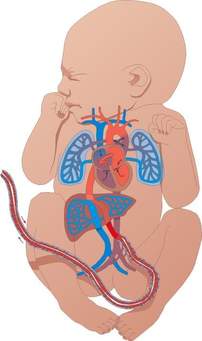
Fetal Circulation q Begins to develop toward the end of third week. q Heart starts to beat at the beginning of the fourth week. Structures involved in fetal circulation 1. Umbilical vein ´ Carries oxygenated blood from placenta to fetus . ´ Number: 1 2. Umbilical artery ´ Carries deoxygenated blood from fetus to placenta. ´ Also known as H ypogastric arteries. ´ Number: 2 3. Ductus Arteriosus: ´ Protect lungs against circulatory overload. ´ Allows right ventricle to strengthen. ´ Carries mostly medium oxygen saturated blood. 4. Ductus Venosus ´ Fetal blood vessel connecting umbilical vein to inferior venacava . ´ Blood regulated via sphincter. ´ Carries mostly high oxygenated blood. 5. Formen Ovale ´ Connect right and left chamber of heart. ´ Transfer highly oxygenated blood from right antrium to left antrium . Fig: Structure of parts involved in fetal circulation Flow chart of fetal circ...