Fetal Circulation | American Heart Association
Fetal Circulation
qBegins to
develop toward the end of third week.
qHeart starts
to beat at the beginning of the fourth week.
Structures
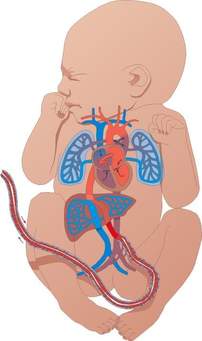
involved in fetal circulation
1. Umbilical vein
´Carries
oxygenated blood from placenta to fetus.
´Number: 1
2. Umbilical artery
´Carries
deoxygenated blood from fetus to placenta.
´Also known as Hypogastric arteries.
´Number: 2
3. Ductus Arteriosus:
´Protect lungs
against circulatory overload.
´Allows right
ventricle to strengthen.
´Carries mostly
medium oxygen saturated blood.
4. Ductus Venosus
´Fetal blood
vessel connecting umbilical vein to inferior venacava.
´Blood
regulated via sphincter.
´Carries mostly
high oxygenated blood.
5. Formen Ovale
´Connect right
and left chamber of heart.
´Transfer
highly oxygenated blood from right antrium to left antrium.
Fig: Structure of parts involved in fetal circulation
Flow chart of fetal circulation
Umbilical veins carries oxygenated blood from placenta to fetus.
⇙ ⇘
70-80% of oxygenated blood 20-30% of oxygenated blood
goes to liver through portal vein. mixed with inferior venacava and
⇓ forms ductus venosus.
Blood in liver comes out through ⇓
hepatic vein and mix with inferior
venacava.
⇘ ⇙
Goes to Right Antrium.
⇓
Foramen ovale allows the mixed blood to pass to the right ventricle and left antrium by passing through lungs.
Right ventricle Left Antrium
⇙ ⇘
Goes to pulmonary artery by passing Enter to left ventricle.
through lungs.
⇓ ⇓
Mixed blood Passes to Aorta through Mixed blood passes
ductus arteriousus. to aorta.
⇘ ⇙
Mixed blood distributes to the fetal tissues and other body parts.
⇓
Fetal tissues uses oxygen saturated blood.
⇓
Remaining deoxygenated blood carried by two umbilical arteries to placenta from fetal tissues.
⇓
Placenta transfers deoxygenated blood to maternal circulation and gets oxygenated blood.
⇓
Umbilical vein carries the oxygenated blood and the process gets continued.
Changes in circulatory system after birth
- The placenta is replaced by the lungs as the respiratory organ.
- The lungs and the pulmonary vessels expand thereby significantly lowering the resistance to blood flow.
- Subsequently the pressure in the pulmonary artery and right side of the heart is decreased.
- Pressure in the left side of the heart is increased.
- The increasing pressure of left side of the heart decreases the vascular resistance of lungs therefore blood enters to lungs as a respiratory exchange.
Changes in shunts after birth
- Closure of Ductus venosus
- Closure of Ductus Arteriosus
- Closure of Foramen ovale
Overview of Fetal Circulation







Comments
Post a Comment